The Ichimoku Cloud is a technical indicator that tries to quantify support and resistance, it identifies the direction of the trend, and measures the momentum to create potential trading signals. The original name of this indicator was the Ichimoku Kinko Hyo which translates to English as “one look equilibrium chart”. This name tries to express that a technical trader can identify the trend on a chart with one quick look at it. It was created by Goichi Hosoda and was first published in his book in 1969. The Ichimoku Cloud can give well defined signals.
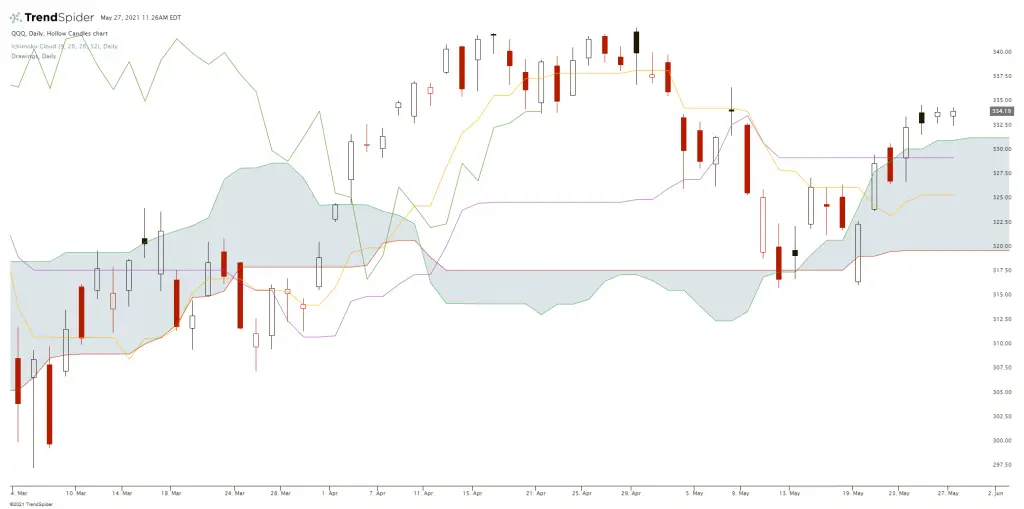
Chart courtesy of TrendSpider.
Four out of the five plots used to create the Ichimoku Cloud derive from the average of the high and low over a time period.
- Conversion Line: (9-period high + 9-period low)/2)). The default setting is 9 periods. On a daily chart, this line is the midpoint of the 9-day high-low range.
- Base Line: (26-period high + 26-period low)/2)) The default setting is 26 periods. On a daily chart, this line is the midpoint of the 26-day high-low range.
- Leading Span A: (Conversion Line + Base Line)/2)) This is the midpoint between the Conversion Line and Base Line. The Leading Span A forms one of the two cloud boundaries. It is called “Leading” because it is plotted 26 periods in the future and forms the faster cloud boundary.
- Leading Span B: (52-period high + 52-period low)/2)) On the daily chart, this line is the midpoint of the 52-day high-low range. The default calculation setting is 52 periods. The value is plotted 26 periods into the future and creates the slower cloud boundary.
- Lagging Span: Close plotted 26 days in the past. The default setting is 26 periods.
The “cloud” part of this indicator on the chart that is made up of the Leading Span A and Leading Span B lines, this is used to identify the overall trend of price action. The correlations between the price, the Conversion Line, and the Base Line are then used to identify the shorter-term trading signals for the swings inside the larger trend. This is way to identify the path of least resistance.
There are two options for identifying the larger trend on a chart using the cloud. One is that the trend is up simply when prices are above the cloud and the trend is down when prices on the chart are below the cloud and the chart is range bound when the prices are inside the cloud itself. The other way to read a chart using the Ichimoku Cloud is to look at the uptrend is strengthened when the Leading Span A (or green cloud outline) is ascending and higher than the Leading Span B (or red cloud outline). This situation produces a green cloud uptrend signal. The inverse of that is a downtrend has a stronger signal when the Leading Span A (or green cloud outline) is descending and lower than the Leading Span B (or red cloud outline). This set up on the chart creates a red cloud signal, because the cloud is shifted forward for 26 days, it also creates a leading indicator for high probability future support or resistance.